请 更新浏览器.
发现
- 去找1支出 on local commerce declined simultaneously across 城市, with extreme declines most likely in low-income neighborhoods.
- 去找2本地在线商务支出增长了1%.5 percent as offline declined sharply, and the online share of LC spend grew by 4.6个百分点.
- 去找3 只有杂货店和药房的支出出现实质性增长, with online growth at least three times greater than offline growth.
- 去找4 Approximately 8 percent of LC spend shifted from restaurant to grocery spend; local access to groceries varied widely by neighborhood income quintile and across 城市.
新型冠状病毒肺炎迅速改变了人们的日常生活. While the scope of the pandemic is global, consumers experience the economic impacts locally. Understanding the strain of 新型冠状病毒肺炎 on the local economy requires a place-based view of the interplay between consumers and merchants within communities, which can inform ongoing efforts to aid the recovery of local economies.
This insight leverages a local commerce dataset of approximately 450 million monthly credit card transactions from a sample of 11 million de-identified 追逐 customers each month between October 2019 and March 2020. The local commerce view represents everyday goods and services transacted between local buyers and sellers and includes the channel by which the transaction was made (online/offline) and the zip code of both the consumer and the merchant, providing an understanding of the distance between a consumer’s residence and where they made a purchase.
The aim of this insight is to inform the impact of the pandemic on the supply and demand of local commerce across U.S. 城市, including analyses of high-income versus low-income neighborhoods, 获取食物, 购买产品和服务类型的变化, 并从实体店转向网络店.
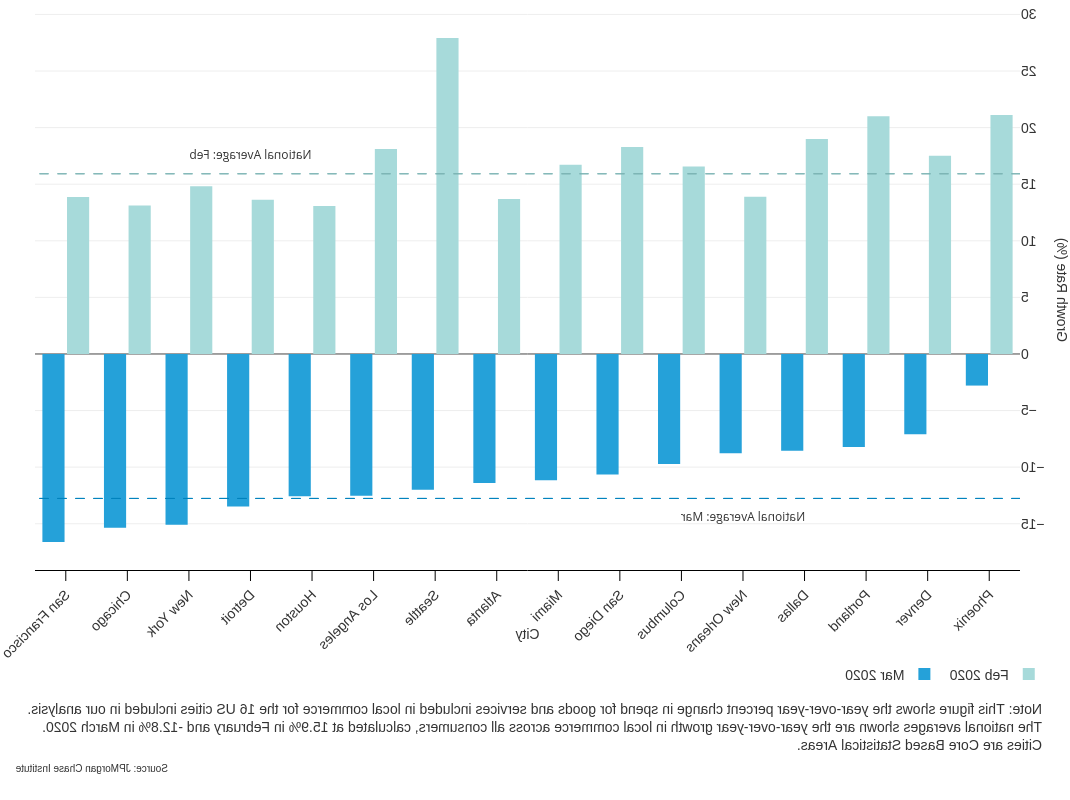
找到一个: 支出 on local commerce declined simultaneously across 城市, with extreme declines most likely in low-income neighborhoods.
- 当地商业支出下降了12%.2019年3月至2020年3月期间为8%.
- 旧金山, 芝加哥, 纽约, and Detroit experienced the sharpest declines in local commerce spend.
- Lower-income neighborhoods experienced a disproportionate share of severe spending declines over 15 percent.
Year-over-year percent change in local commerce spend, by city
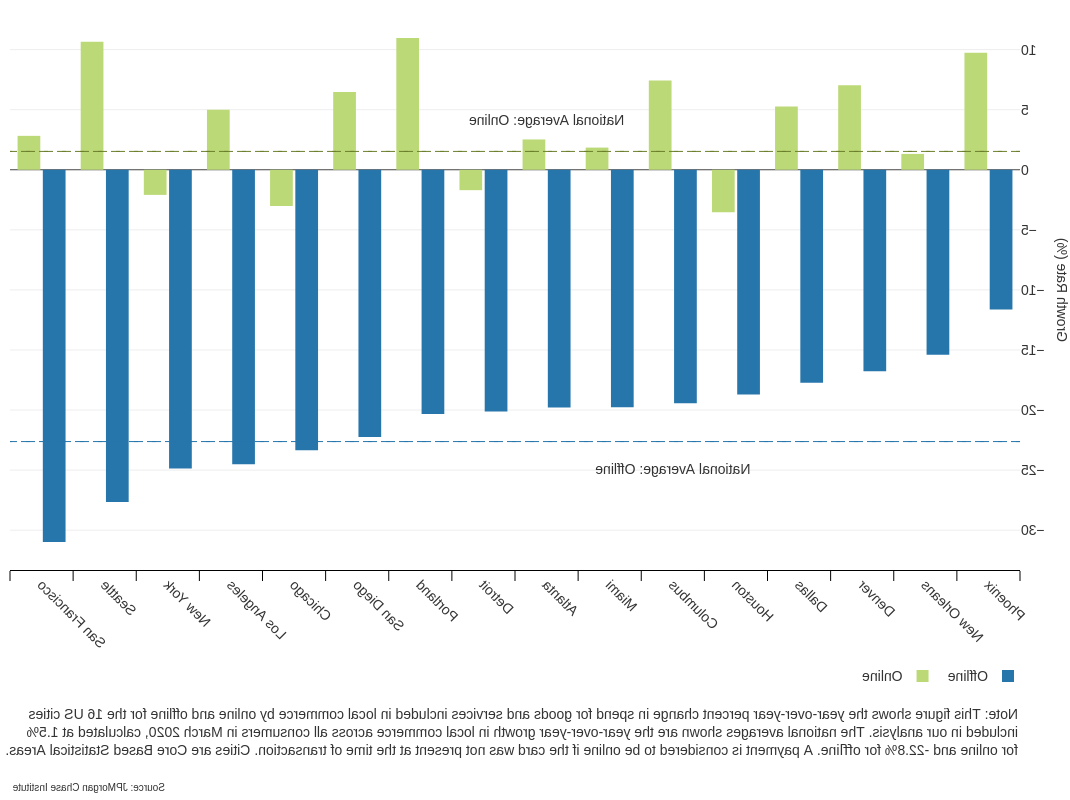
发现二: 本地在线商务支出增长了1%.5 percent as offline declined sharply, and the online share of LC spend grew by 4.6个百分点.
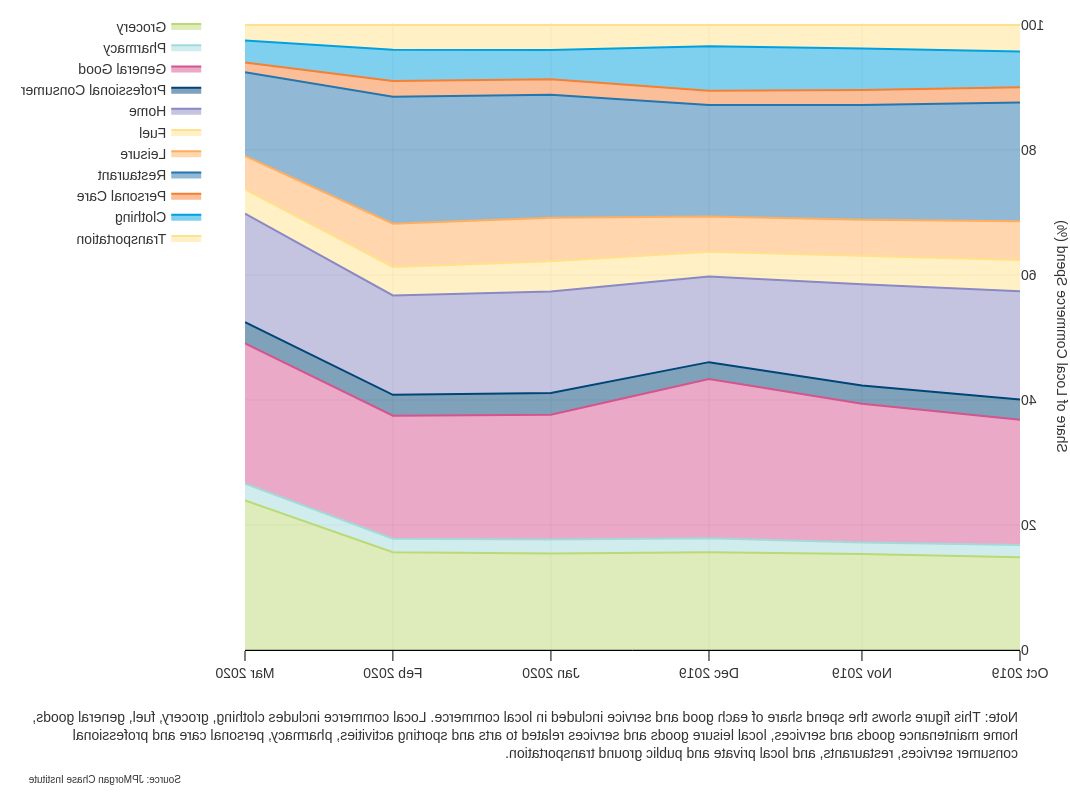
发现三: 只有杂货店和药房的支出出现实质性增长, with online growth at least three times greater than offline growth.
- The share of local commerce spend at grocery stores and pharmacies grew from 15.6%降至23%.9%和2%.2%到2%.2020年2月至3月期间分别为7%.
- 食品杂货的网上消费增长了两倍多.
- Online and offline spending fell for clothing, personal care, leisure, and transportation.
Year-over-year percent change in local commerce spend, by product category
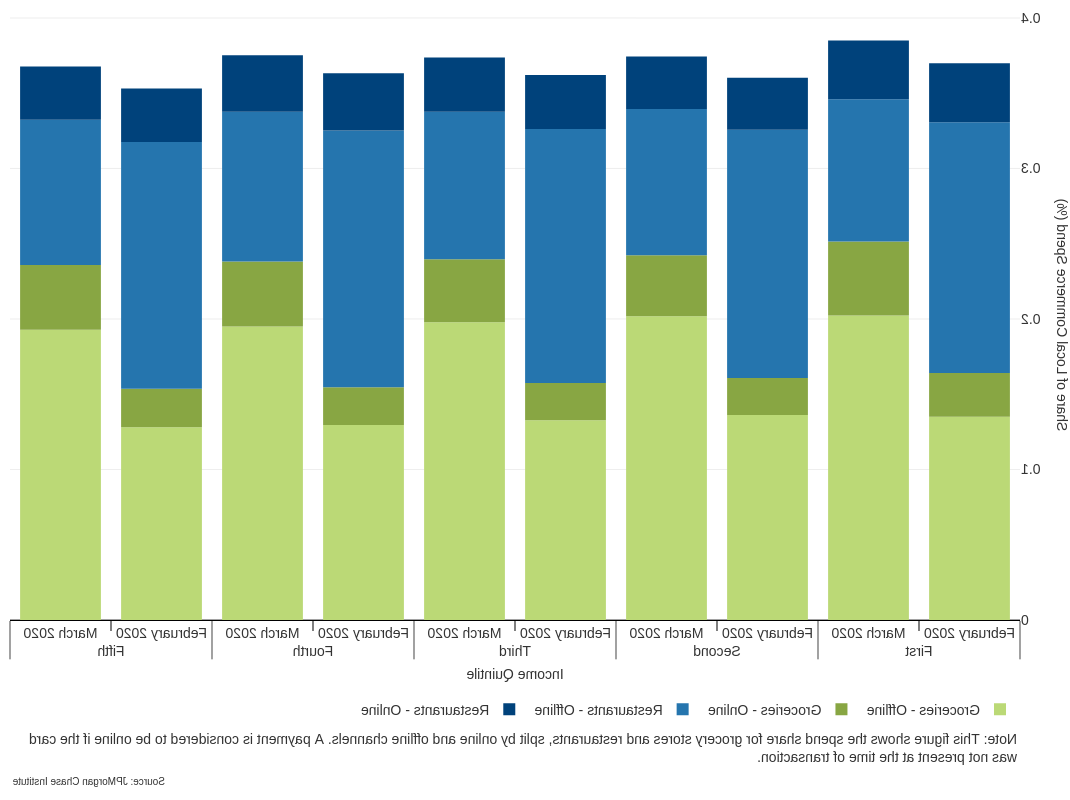
发现四: Approximately 8 percent of LC spend shifted from restaurant to grocery spend; local access to groceries varied widely by neighborhood income quintile and across 城市.
- The share of local commerce spend allocated to groceries grew from 16% in February to 24 percent in March. 餐馆的份额从20%下降到13%.
- Residents of low-income neighborhoods tended to live farther from their grocery stores, and utilize online grocery to a lesser extent than their higher-income counterparts. Both factors increase the time away from home when purchasing groceries.
Spend share for grocery stores and 餐厅, by online and offline channels
作者
Chris O. 小麦: 12bet官方研究所
马文米. 病房小.: 12bet官方研究所
林赛E. 伦敦经济学院 &
经济表现中心